We respond sensitively to your skin concerns
Allergies are exaggerated immune responses in which the body mistakenly identifies harmless environmental substances as dangerous and reacts defensively. An allergy typically begins with sensitization — the first contact with the allergen. Allergies are classified into four types.
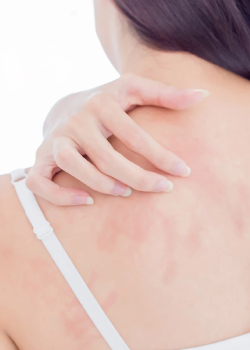
The most common are immediate-type allergies (Type I), which include hay fever, allergic asthma, and hives (urticaria). In these cases, allergens bind to antibodies, triggering the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators.
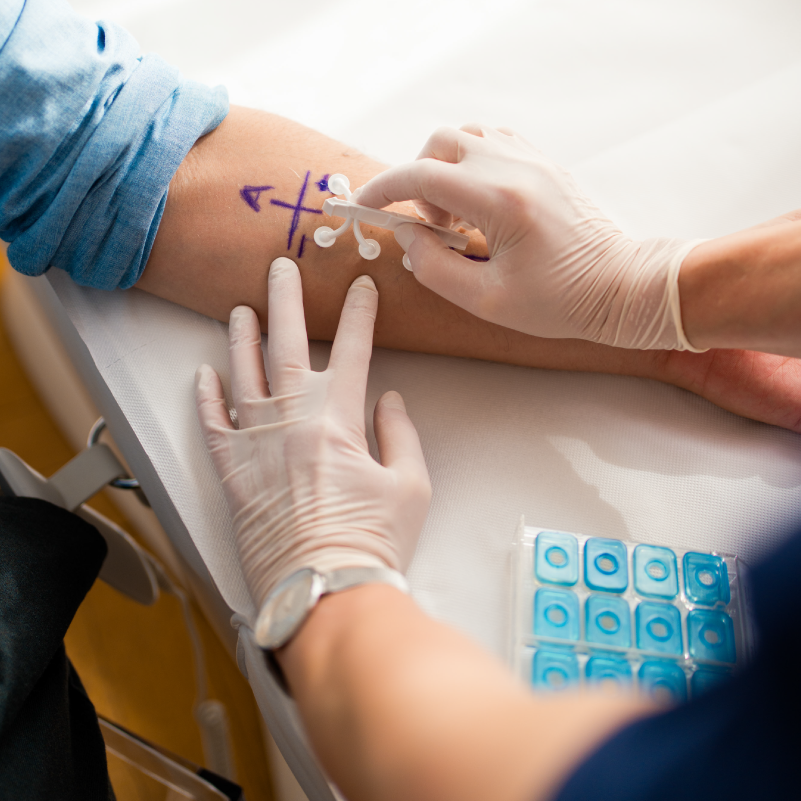
Contact allergies, on the other hand, belong to the delayed-type (Type IV). Here, inflammation occurs 12 to 72 hours after exposure to the allergen.
Less common are Type II and Type III allergies, which include, for example, transfusion reactions. In these types, antibodies bind to cell-bound antigens, forming immune complexes that can block small blood vessels and cause tissue damage.



Doctors with Heart and Experience
Modern Dermatology & Aesthetics
Heilwigstraße 33, 20249 Hamburg
We use cookies to optimize our website and our service.
Under settings, you will find detailed information and can make your choices. You can revoke or adjust your selection at any time in the cookie manager at the bottom right of the page.